Calculate Latency By Distance
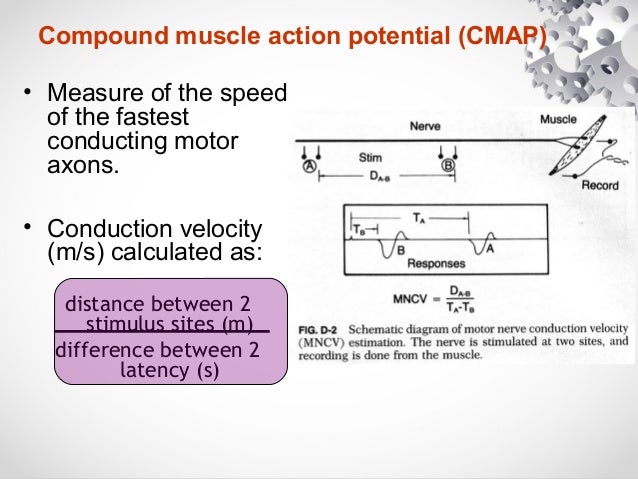
Latency = latency atelectrode R1 (ms)d = distance (mm) from stimulating electrode to recording electrodeR1Velocity = d /latency (m/s) or (mm/ms)One can also calculate the velocity forelectrode R7: the same formula applies except that the distance d andthe latency are of course longer.Questions andanswersQ: How do the absoluteand difference methods for calculating velocity compare? What errors are involved indetermining velocity with the frog sciatic nerve preparation?A: By using the difference method, you subtract out any'uncertainties' involved in the measurement of latencies. For example, ifwe are uncertain as to where the AP's are actually originating within the vicinity of thestimulating electrodes, this 'error' will be introduced into both latencymeasurements, and therefore subtracted out when performing a difference methodcalculation. However, the difference method is only experimentally sound when one isdealing with the same population of nerve fibres over the recording electrodes used, whichis not the case with the sciatic nerve, as it is a short nerve, and thin at one end.The non-uniformity of the nerve, and the difficulty inmaking accurate measurements of very small distances and latencies are principal points toconsider when making conduction velocity measurements. Naturally if the nerve studied werelonger and more uniform, we would improve the accuracy of our calculations.Q: Could we just as easily have measuredvelocities by taking a latency measurement to the peak of the negative phase of the CAP(instead of to the peak of the positive phase)?A: We could dothe measurement using the peak of the negative phase of the CAP, but the negative phase isoften smaller, overlapping with the positive phase, thus making measurements moredifficult. If we did measure the latency at the negative phase, it would be a latencycorresponding to the second recording electrode, and distance measurements wouldthen have to be taken accordingly.

Calculate Latency By Distance Formula
Fiber Latency Over Distance
In many cases, that adds a millisecond to the ping results, above and beyond the latency of the network itself. The biggest factor in typical WAN latency is the speed of light, through fiber-optic cable, which is about 124 miles per millisecond. Network Latency Formula/Equation. Following equations or formulas are used for this network latency calculator. Useful converters and calculators. Following is the list of useful converters and calculators. DBm to Watt converter Stripline Impedance calculator Microstrip line impedance Antenna G/T Noise temp. RELATED LINKS.